Digital transformation is reshaping industries worldwide, including forestry. While digital technologies hold immense potential for efficiency, sustainability, and competitiveness, their adoption across the European forestry sector remains uneven and inadequately monitored. 4Growth addresses this challenge by innovatively leveraging web scraping and artificial intelligence (AI) to generate valuable insights into the adoption and impacts of digital technologies in the forestry sector. Our project partners VTT have been designing and implementing novel methods for extracting insights from web data, for instance the large-scale Europe wide project where 200 thousands firms across Europe were looked at to identify their innovative activity [1], as well as mapping the Finnish ecosystem on innovative and collaborative efforts with utilisation of large language models and knowledge graphs [2].
Traditional data collection methods, such as surveys and interviews, are valuable but often constrained by resources and scalability. Many forestry companies, however, maintain websites that serve as rich sources of publicly available information about their operations, innovations, and technological advancements.
By automating data collection through web scraping, 4Growth efficiently gathers relevant information from numerous company websites. This approach allows for a broader and more systematic assessment of digital adoption trends without the limitations of manual data collection.
The data collection process began with the identification of a diverse sample of forestry-related companies across the European Union. Companies were selected using the Orbis database and categorised by NACE [3] codes spanning industries such as logging, sawmilling, pulp production, and forestry-focused technology providers. Web scraping systematically navigated company websites, extracting textual content for AI-driven analysis.
Given the vast volume of data collected, AI, specifically Large Language Models (LLMs), was employed to interpret and categorise the information. Specifically, the Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) method allowed for sophisticated natural language processing, enabling the extraction of insights aligned with predefined analytical criteria. This automated approach helped answer survey-like questions without the need for direct industry engagement.
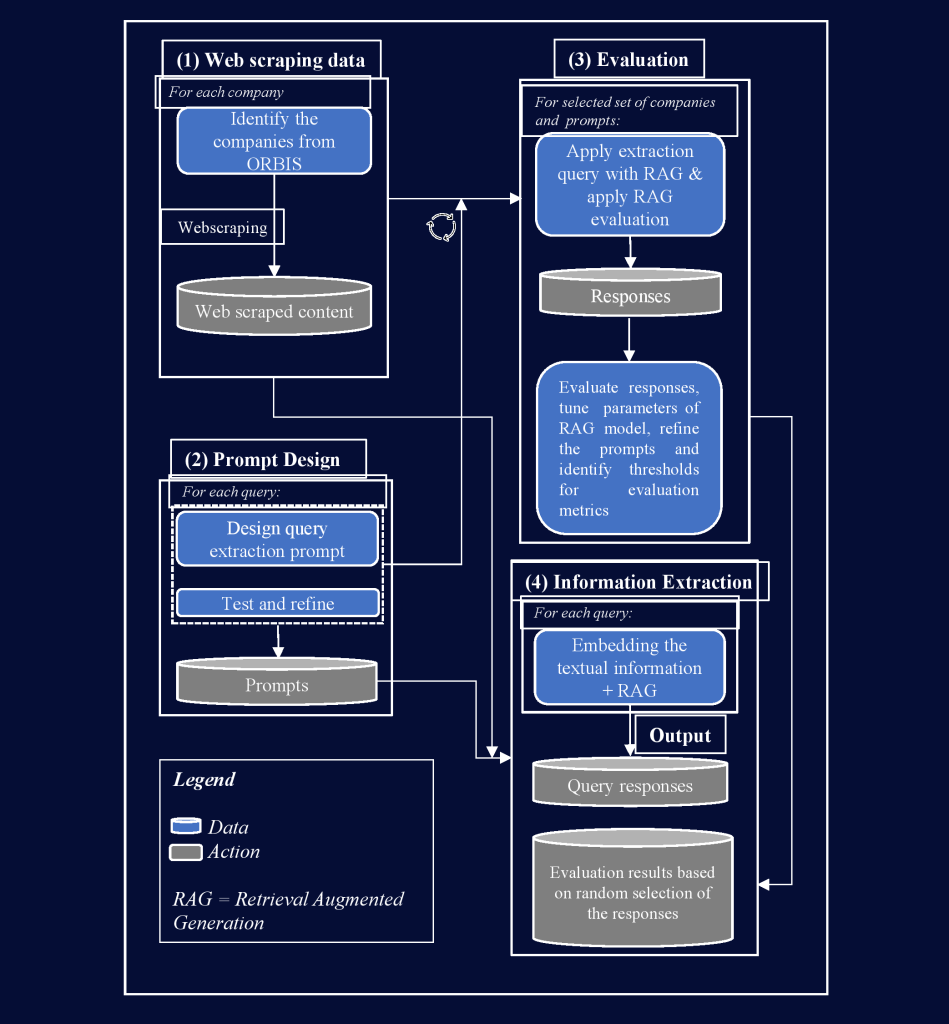
To maintain reliability and precision in AI-driven analysis, key performance metrics were implemented:
Preliminary findings from the automated analysis revealed compelling trends in digital technology adoption within the forestry sector.
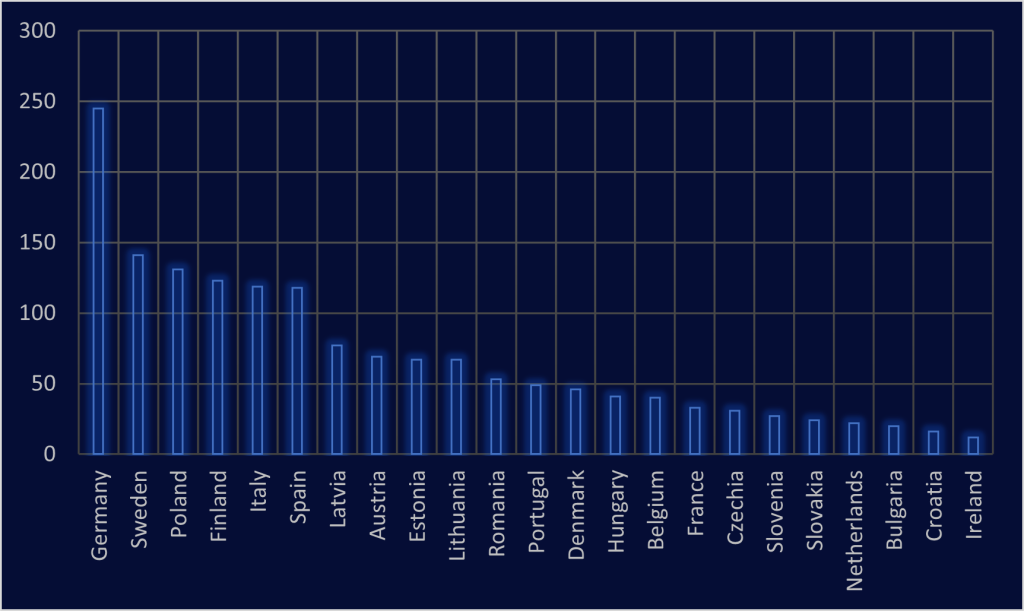
Number of companies by countries in the analysis
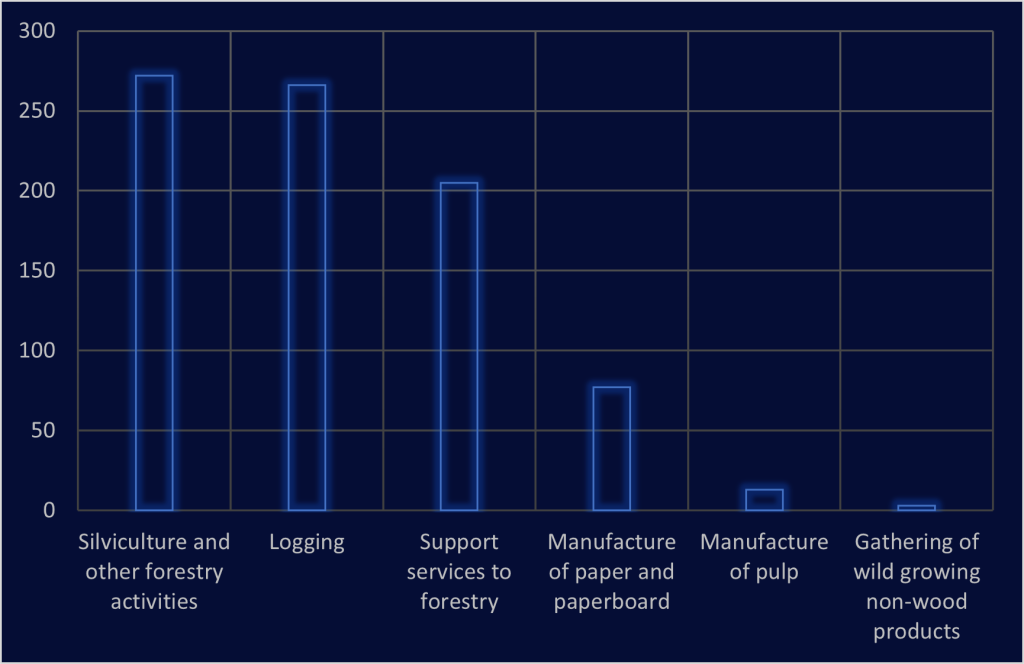
Number of companies by NACE classification in the analysis
Many companies publicly disclosed information on their core activities, governance models, and data management practices. However, detailed discussions on challenges and economic impacts related to digital technology adoption were scarce.
This pattern suggests that while companies are eager to showcase technological achievements, they may be less willing to highlight operational difficulties. As a result, automated methods like web scraping provide valuable industry-wide snapshots but may need to be complemented by traditional surveys to capture more nuanced perspectives.
Despite its effectiveness, web scraping encountered several obstacles:
These challenges highlight the need for ongoing refinement in web scraping methodologies and AI-driven analysis.
Despite these hurdles, insights derived from web scraping significantly contribute to the 4Growth project’s broader objectives. The findings directly feed into the project’s Market Monitoring & Forecasting Tool (MMFT), foresight modules, and impact assessment frameworks.
Future improvements will focus on refining web scraping techniques and enhancing AI models. Adjusting the depth of data extraction and fine-tuning AI analytical parameters can further boost accuracy and reliability. Additionally, integrating adaptive learning mechanisms within AI tools will help manage evolving industry terminology and website structures more effectively.
Beyond forestry, these automated data collection methodologies have the potential to support digital transformation monitoring in agriculture. As AI technologies advance, deeper analytics and predictive capabilities will further enrich our understanding of digital adoption across multiple industries.
By harnessing AI and web scraping, the 4Growth project is pioneering an innovative approach to tracking digital transformation in forestry. Automated data collection provides scalable, real-time insights that complement traditional research methods, ultimately paving the way for better-informed policy-making, strategic interventions, and industry-wide innovation. As these methodologies continue to evolve, they will play an increasingly vital role in shaping the future of digital adoption in forestry and beyond.
[1] https://cris.vtt.fi/en/projects/addressing-productivity-paradox-with-big-data-implications-to-pol
[2] https://cris.vtt.fi/en/equipments/sfinno-20-advancing-the-database-of-finnish-innovations
[3] NACE codes (Nomenclature statistique des activités économiques dans la Communauté européenne) are a standardised classification system used by the European Union to categorise economic activities for statistical and administrative purposes. https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/web/nace